Eli lilly
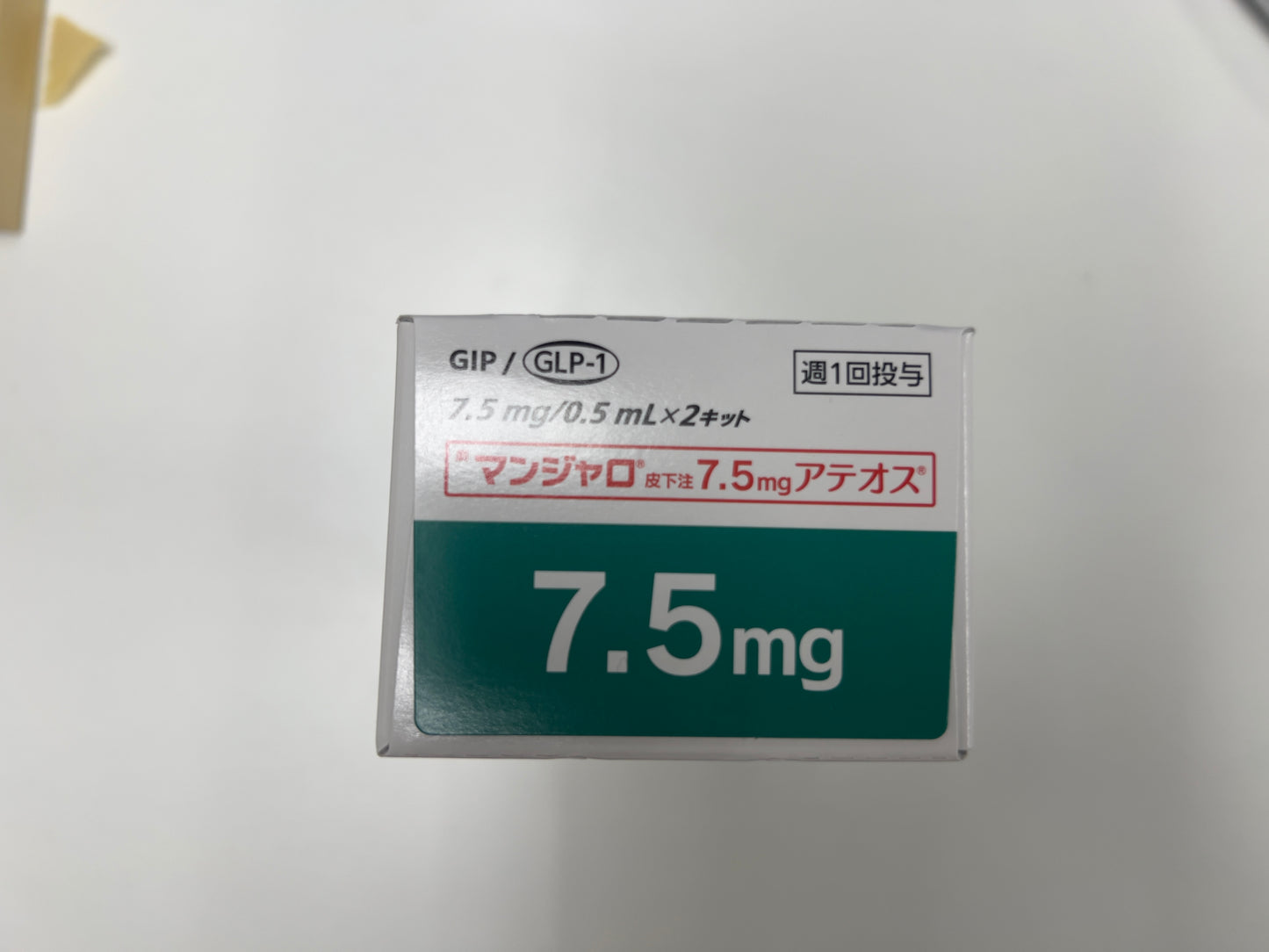
Tirzepatide Injection 7.5mg
Tirzepatide Injection 7.5mg
Impossible de charger la disponibilité du service de retrait
Key Selling Points of Tirzepatide for Diabetes and Obesity Management
1. Innovative Dual Receptor Mechanism
• First-in-Class Dual Agonist: Tirzepatide is the world’s first dual agonist of glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptors.
◦ GLP-1 Receptor: Delays gastric emptying, inhibits glucagon secretion, and stimulates insulin release to lower blood sugar.
◦ GIP Receptor: Enhances insulin sensitivity, promotes fat metabolism, and increases energy expenditure, synergizing with GLP-1 for superior metabolic control.
• Precision Metabolic Regulation: Mimics natural GIP/GLP-1 pathways to simultaneously improve glycemic control, reduce weight, and optimize lipid/energy balance.
2. Clinically Proven Efficacy
• Exceptional Blood Sugar Control:
◦ Reduces HbA1c by 1.5%–2.0% in type 2 diabetes patients, outperforming many single-receptor therapies.
◦ Helps patients achieve glycemic targets faster, even when prior treatments fail.
• Powerful Weight Loss:
◦ Leads to 15% or more weight reduction in obese/overweight patients in long-term studies, with sustained effects.
◦ Suppresses appetite and increases satiety, addressing the root cause of overeating.
• Cardiovascular & Metabolic Benefits:
◦ Lowers triglycerides, LDL cholesterol, and blood pressure, reducing cardiovascular risk.
3. Convenient and Patient-Friendly Administration
Function and Indications
Indicated as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus by mimicking the action of natural GIP and GLP-1, promoting insulin secretion, inhibiting glucagon release, and delaying gastric emptying.
Applicable Population
• Primary Use: Adults with type 2 diabetes who have inadequate glycemic control through lifestyle modifications alone.
• Additional Use: Adults with obesity (BMI ≥28 kg/m²) or overweight (BMI ≥24 kg/m²) and at least one weight-related comorbidity (e.g., hypertension, dyslipidemia, obstructive sleep apnea), for weight management.
Contraindications
• Personal or family history of medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC) or multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome type 2 (MEN 2).
• Hypersensitivity to tirzepatide or any excipients.
Usage and Dosage
• Starting Dose: 2.5 mg once weekly, administered subcutaneously.
• Dose Titration: After 4 weeks, increase to 5 mg/week; may further increase by 2.5 mg/week (to a maximum of 15 mg/week) based on glycemic control or weight loss response.
• Administration: Inject into the abdomen, thigh, or upper arm; rotate injection sites to avoid skin reactions.
Adverse Reactions
• Common (≥5%): Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, constipation, headache, fatigue.
• Serious Risks:
◦ Thyroid C-cell tumors: Observed in animal studies; contraindicated in patients with MTC history/family history.
◦ Hypoglycemia: Increased risk when combined with insulin secretagogues (e.g., sulfonylureas) or insulin.
Partager